Just as the old saying goes: it’s the little things that make the biggest impact. This is especially true when it comes to design a data center—there are so many factors to consider during the process, among which the proper cabling pathway construction only possesses a small part yet matters significantly. Data center designers are always aware of that multiple products must work together to ensure a successful pathway and cable management. This article will take a review of the commonly seen cabling pathway types.
What Is Cabling Pathway?
Cabling pathways allow the placement of data center trunk cables and cross-connect cables between racks and cabinets. Cabling pathway comes into two forms: overhead pathway and under floor pathway. Both of them are designed to accommodate all standards-compliant cabling and allow for necessary changes later. In other words, cabling pathway should support the weight of cables in the initial installation and also facilitate additional cables in the future. Which helps ensure robust pathways that respond well to cable work over the facility’s life cycle.
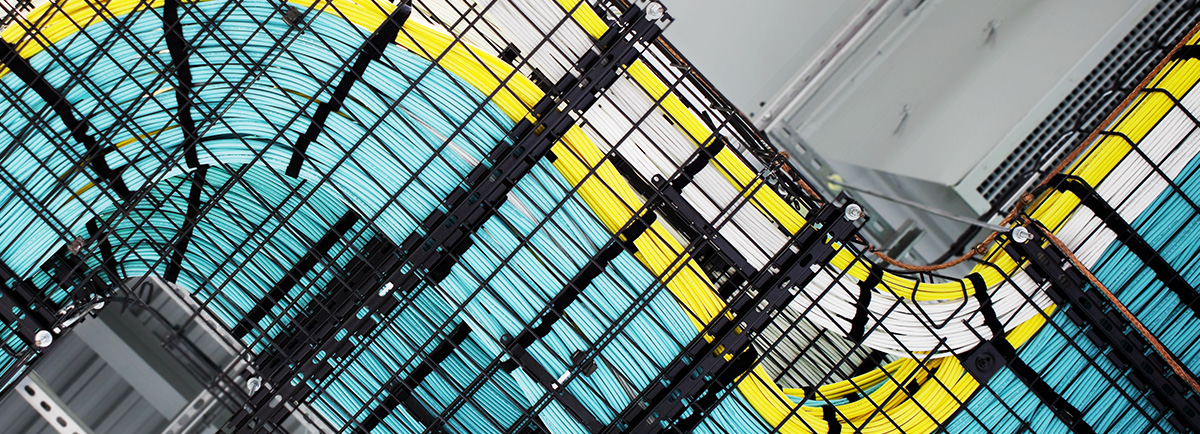

Cabling Pathway types Overview
Cabling pathway types come in a dazzle array of styles, in this section, we’ll illustrate some of them that widely used in work areas, wiring closets and for horizontal and backbone cable runs.
Conduit
Conduits are pipes that cable is placed in and pulled through, and it can be metallic or nonmetallic, rigid or flexible. They run from the telecommunications room to the work area outlets in the floor, walls, or columns of a building. To ensure that enough conduit be installed, it is recommended that the conduit would better be only 40 percent full by your current cable needs, or 60 percent full to the maximum. Which leaves you space for future growth.
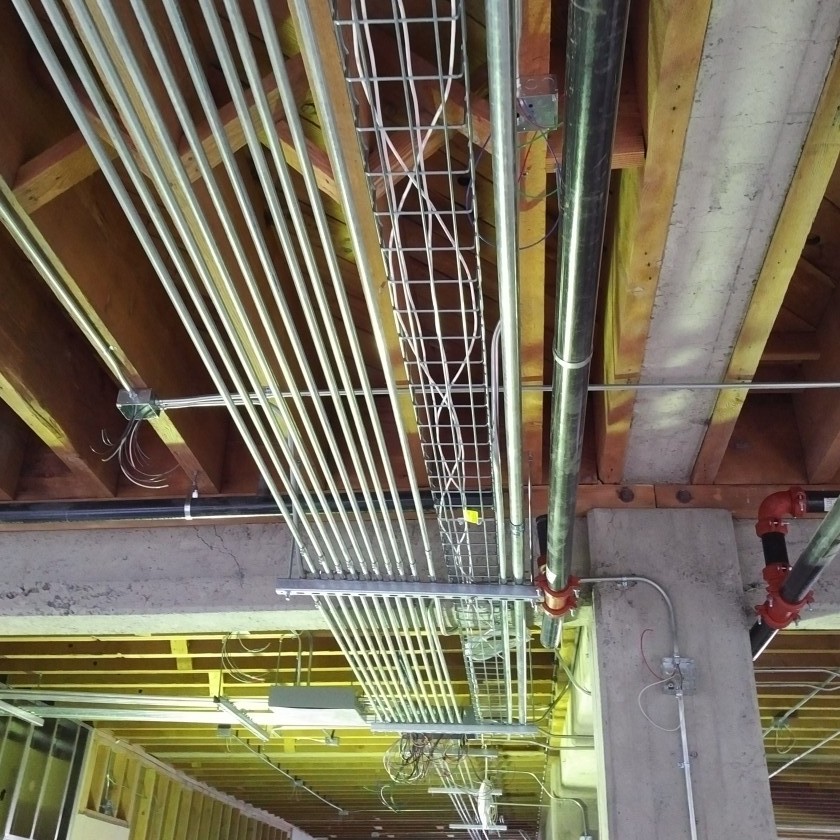

Cable Trays
Cable tray serves as an alternative cabling pathway component to conduit, which can be installed as distribution system to route and support your cables. Typically, cable tray is open and equipped with sides that allow cable to be laid within the tray’s entire length. It is ideal to use cable tray to manage a large number of horizontal cable runs, due to their greater accessibility when it comes to maintenance and troubleshooting, as well as its ability to accommodate change.
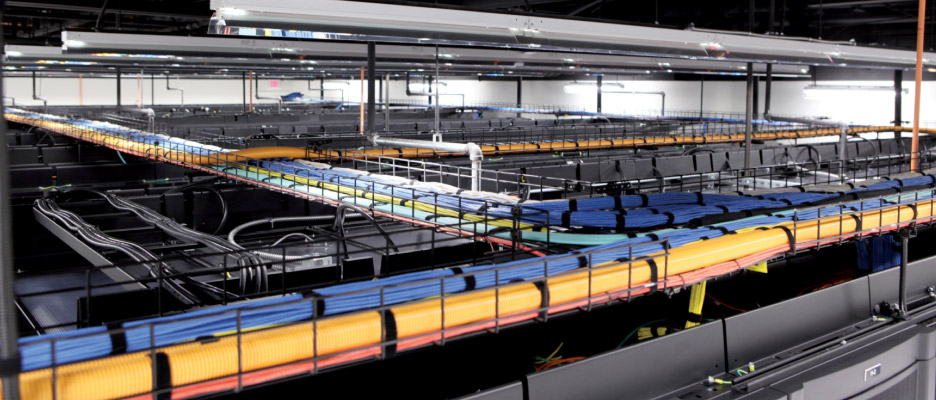

Basket Tray
A basket tray serves as a cable tray that designed for light duty applications, which is lightweight and easy to install. Unlike ladder rack installation, to properly install a basket tray, certain level of experience is needed. Many of the accessories that accompany ladder racks also accompany basket trays, to ensure proper bend radius and a proper transition to the equipment rack.

Underfloor Cable Tray
An underfloor cable tray is used primarily in data centers. It resembles much as overhead support pathway types. However, when using under floor cable tray systems, the air space may be a plenum air space, so all cable and patch cables would need to be plenum to ensure proper air flow.
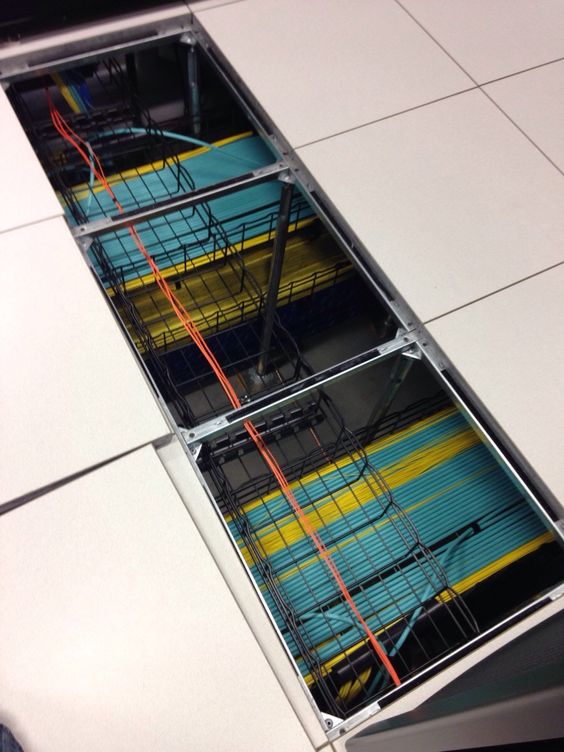

Ladder Racks
A ladder rack is made of tubular steel and comes in sizes from 6’’ to 36’’ wide. The installation of a ladder rack is simple and requires little trade experience. Ladder rack comes with many accessories such as 90-degree bends, waterfalls and cable retaining posts. These accessories allow the routing of cable without damage.
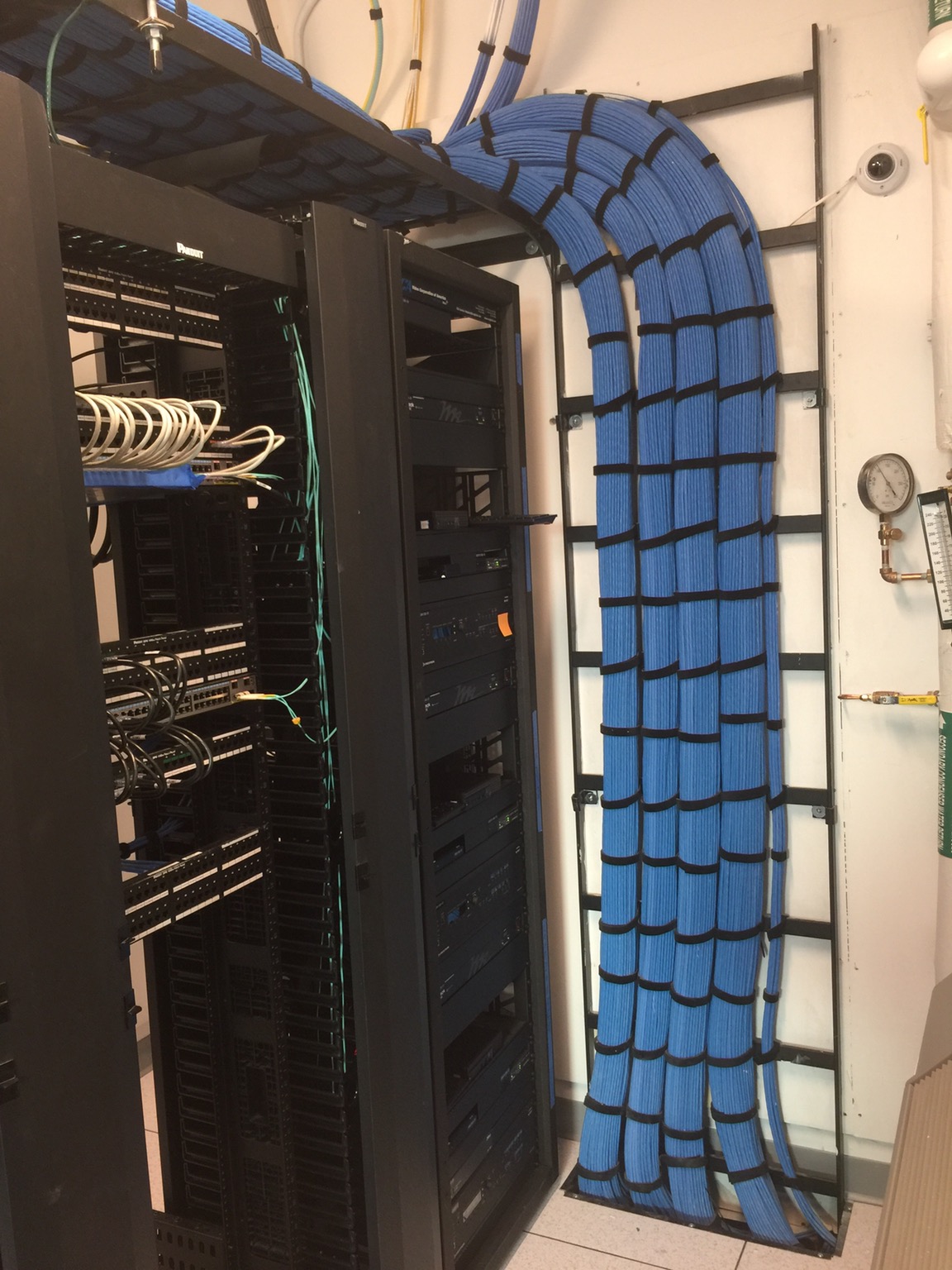

Raceways
Raceways are special types of conduits used for surface mounting horizontal cables. They are usually pieced together in a modular fashion with vendors providing connectors that do not exceed the minimum bend radius. Raceways are mounted on the outside of a wall in places where cable is not easily installed inside the wall. They are commonly used on walls made of brick or concrete where no telecommunications conduit has been installed.

Installation Considerations for Cabling Pathway
With the purpose of supporting the current needs as well as future growth, several essential factors should better be considered while designing and installing cable pathway.
- Overhead and underfloor cabling pathway should be installed in a matrix type method, allowing cables to be routed from point to point anywhere in the data center.
- When installing any types of cabling pathway, grounding and bonding are rather vital. Make sure that all racks, cabinets, and cabling support components are properly bonded and the system is grounded.
- Always leave room for future growth. All cable tray and ladder rack should allow room to accommodate at least 50% growth after the initial install.
- Be sure the heaviest cable in on the bottom of the tray or separated from the lighter cables, and separate the copper cables from the fiber cables if possible.
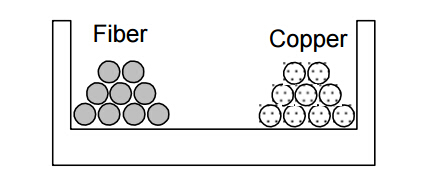
- Avoid mounting any types of cabling pathway in locations that block access to other equipment inside and outside the racks.
- Avoid routing pathways with copper cables near equipment, which may generate high levels of electrometric interference. Avoid areas around power cords, florescent lights, building electrical cables and fire prevention components.
Conclusion
The knowledge concerning different styles of cabling pathway lies the foundation of proper installation of data center pathway. Choosing proper cabling pathway type makes it easier to perform cable-related work and maintenance later. Make your decision on the basis of your unique working condition and environments, and do not forget to account for the factors mentioned below while perform cabling pathway installation.
No comments:
Post a Comment