SDN (Software-Defined Networking) technology is generating huge interest in networking industry due to its ability to add higher agility and scalability for networks. At the core of the SDN technology is the OpenFlow protocol, and SDN with OpenFlow switch promises flexibility and fast configuration of communication networks. So what exactly is OpenFlow and OpenFlow switch? How does OpenFlow switch work to improve network agility and scalability? We try to explain it in detail and clear out the confusions.
What is OpenFlow and OpenFlow Switch?
OpenFlow is a programmable network protocol for SDN environment, which is used for communication between OpenFlow switches and controllers. OpenFlow separates the programming of network device from underlying hardware, and offers a standardized way of delivering a centralized, programmable network that can quickly adapt to changing network requirements.
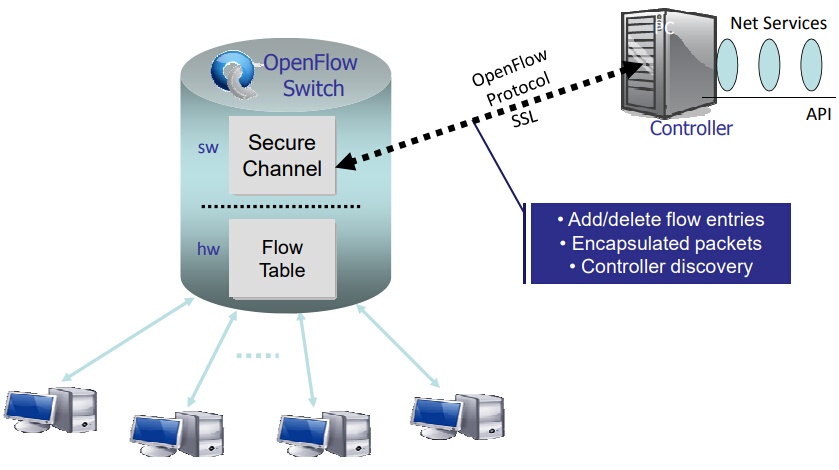
An OpenFlow switch is an OpenFlow-enabled data switch that communicates over OpenFlow channel to an external controller. It performs packet lookup and forwarding according to one or more flow tables and a group table. The OpenFlow switch communicates with the controller and the controller manages the switch via the OpenFlow switch protocol. OpenFlow switches are either based on the OpenFlow protocol or compatible with it.
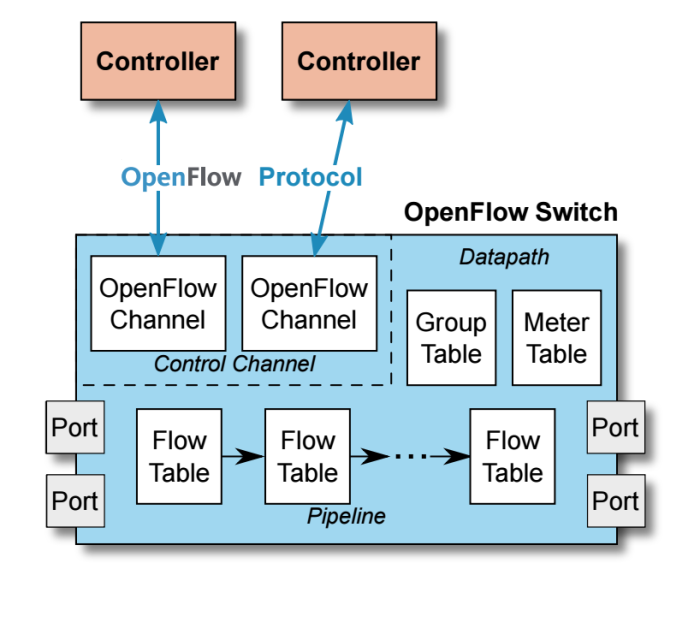
How Does OpenFlow Switch Work?
An OpenFlow switch can only function with the collaborate work of three essential elements: flow tables installed on switches, a controller and a proprietary OpenFlow protocol for the controller to talk securely with switches. Flow tables are set up on switches. Controllers talk to the switches via the OpenFlow protocol and impose policies on flows. The controller could set up paths through the network optimized for specific characteristics, such as speed, fewest number of hops or reduced latency.
OpenFlow Switch vs Conventional Switch: What’s the Difference?
In a conventional switch, packet forwarding (the data plane) and high-level routing (the control plane) occur on the same device. While for an OpenFlow switch, the data plane is decoupled from the control plane: with the data plane implemented in the switch itself but the control plane in software and a separate SDN controller makes high-level routing decisions. The switch and controller communicate by means of the OpenFlow protocol. OpenFlow switch hence boosts the following advantages:
- With OpenFlow switch, the SDN controller could route non critical/bulk traffic on longer routes that are not fully utilized.
- The SDN controller can easily implement load-balancing at high data rates by just directing different flows to different hosts, only doing the set-up of the initial flow's.
- Traffic can be isolated without the need for vlan's, the SDN controller of OpenFlow switch can just refuse certain connections.
- Setup a network TAP/Sniffer easily for any port or even specific traffic by programming the network to send a duplicate stream to a network monitoring device.
- OpenFlow switch allows for the development of new services and ideas all in software on the SDN controller, as well to accelerate new features and services.
Why OpenSwitch Is the New Trend?
OpenFlow switch is designed to provide consistency in traffic management and engineering, by making control function independent of the hardware it's intended to control. This combination of open source software and commodity hardware holds the potential for unprecedented efficiency and operational agility, which fitted well in the world where network becomes increasingly diverse and demanding. Enabling OpenFlow on physical switches and move to OpenFlow switch is something that most clients have been working toward. FS.COM switch product line consists of 10GbE switch, 40GbE switch and 100GbE switch that supports OpenFlow 1.3, which can be used as OpenFlow switches in open networking environment.
10G SDN Switch with L2/L3 ICOS, 48*10GbE ports + 6*40GbE ports
|
|
40G SDN Switch L2/L3 ICOS, 32*40GbE ports
|
|
100G L2/L3 Switch Loaded with ICOS, 48*25GbE ports +6*100GbE ports
|
Conclusion
OpenFlow switch addresses bottlenecks to high performance and scalability in SDN environments. Providing an efficient, vendor-independent approach to managing complex networks with dynamic demands, OpenFlow switch is likely to become commonplace in large carrier networks, cloud infrastructures, and other networks. FS.COM SDN OpenFlow switch has received great reputations from our customers, for more information, just reach us via sales@fs.com.